x <- 55
x[1] 55In the first part of Session 1, we will introduce the tools used in this course. We will primarily be working in Posit Workbench, but it is important to know how to install and use the tools on your own as well for future use.
If this is your first time learning to program, you might find it overwhelming at first. That is okay, and to be expected. Programming is best learned by doing, doing repeatedly, and looking up how to do. Keep going, ask questions, and refer often to the resources provided in this course.
Stop and ask questions anytime! I am gearing this material to new learners of R but as an advanced user myself it is possible I can overlook something that I need to explain in more detail. Please stop me and ask if anything is unclear!
Some of the topics covered here will be more or less useful to each of you, depending on the type of work you do and how much and what type of data are involved. But all of it will help you have a strong foundation even if the specific topics here are not directly applicable in your field.
R and RStudio are two separate things, and to use both you will need to install two programs onto your personal computer.



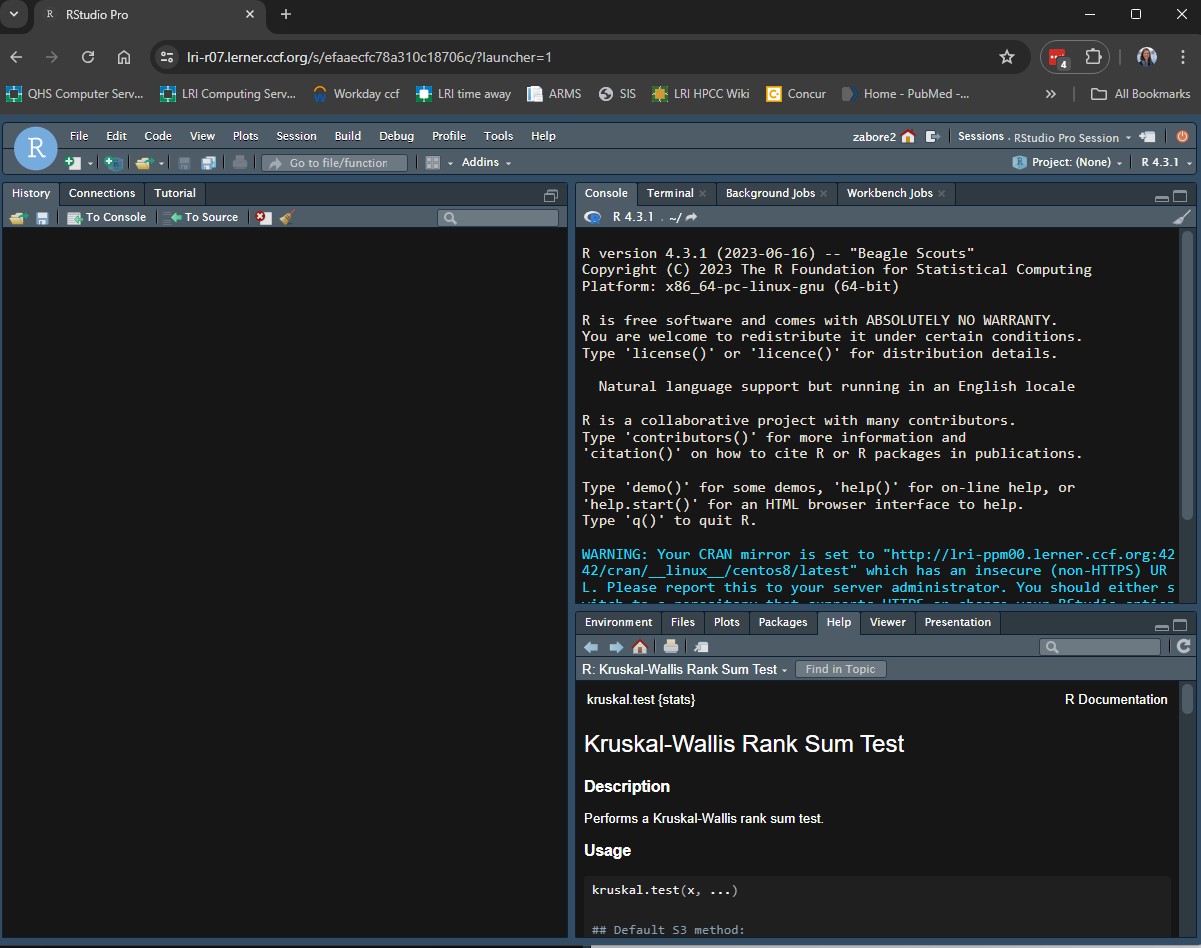
The layout of the panes can be customized by going to Tools > Global Options > Pane Layout. I can help you customize as well if there are things you prefer, just ask!
Text editor (i.e. R script) - this is where you will type your code, and you will save this file to a project folder for reproducibility
Console - this is where the code will be executed
Other panes will contain a variety of tabs. Some to note include:
Always use a text editor to type code so that it can be saved for reproducibility purposes.
How to open a text editor window:
To send this to the console to be executed, you can do one of the following:
Use the assignment operator <- to assign values to objects
<- assigns the value on the right, to the object on the leftTo assign a character variable, wrap it in single or double quotes:
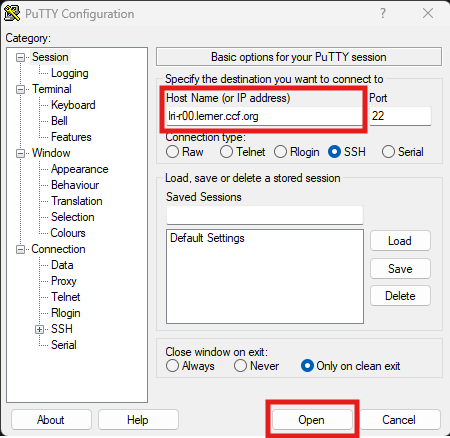
Login to Posit Workbench and start a new RStudio session.
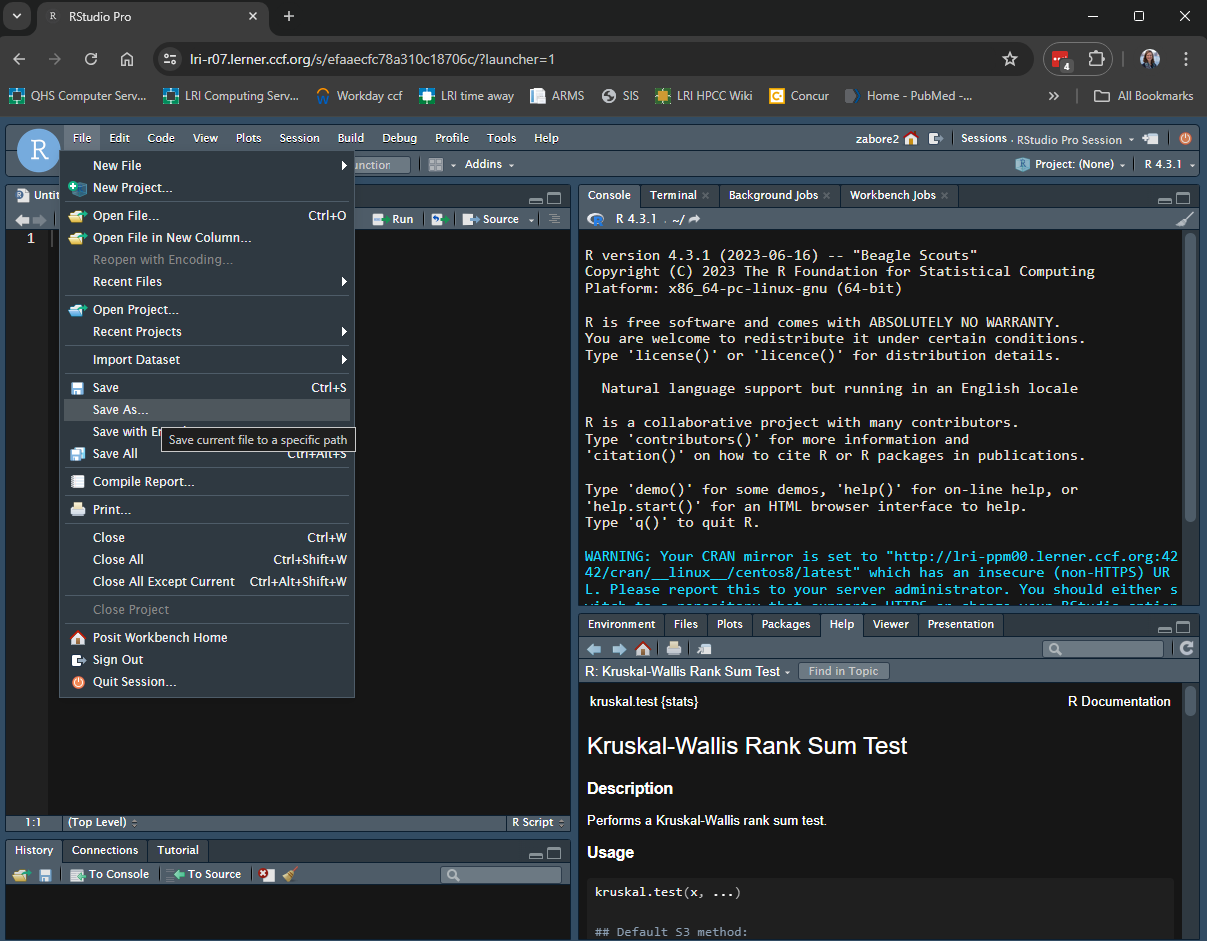
Go to File > New File > R Script to open a new, blank R script
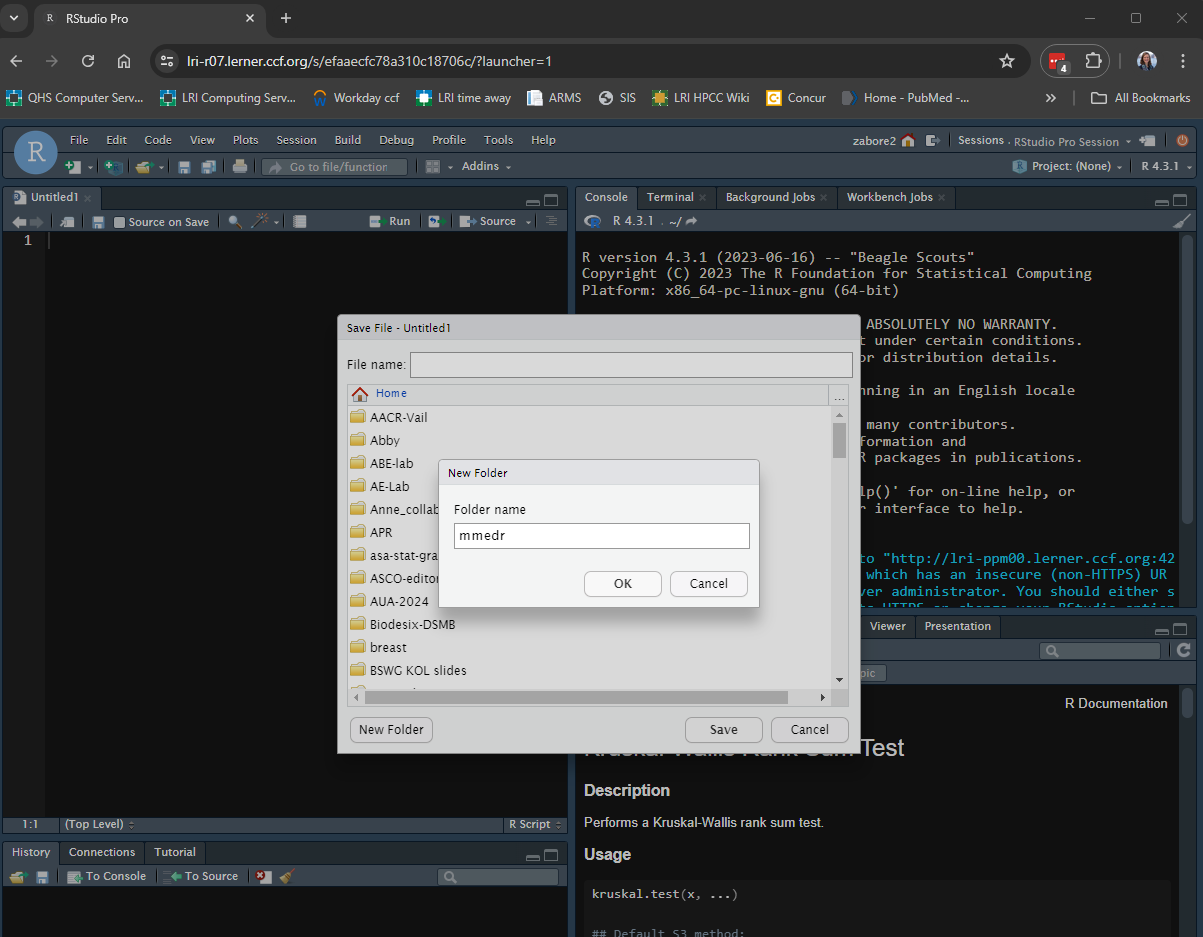
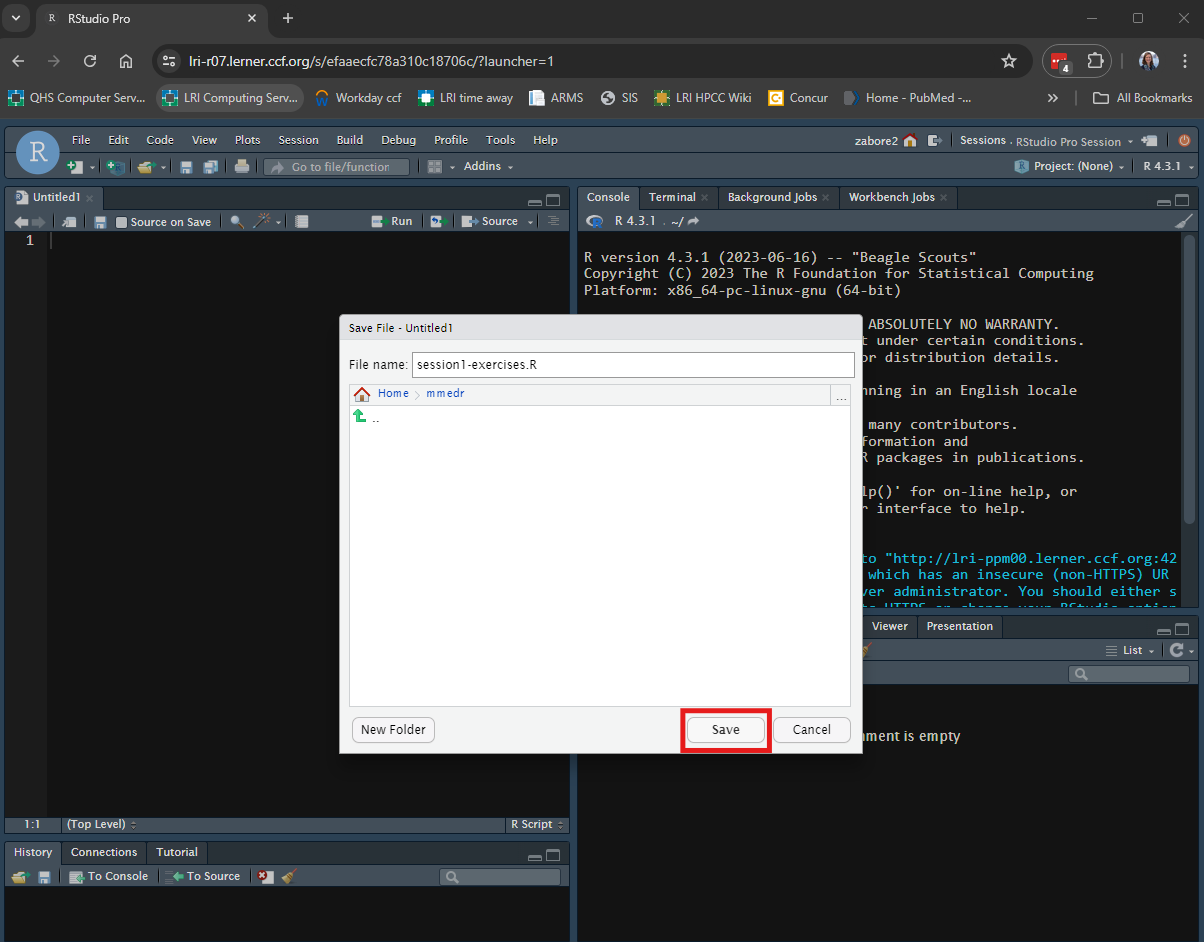
Save the file to a new folder on your home directory called “mmedr” with the name “session1-exercises.R”